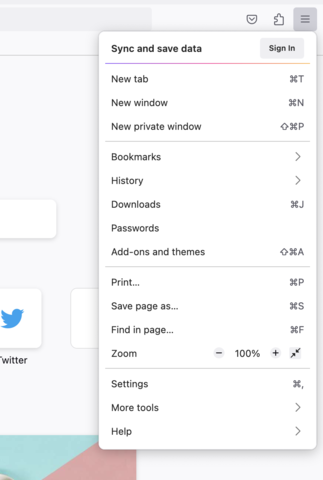
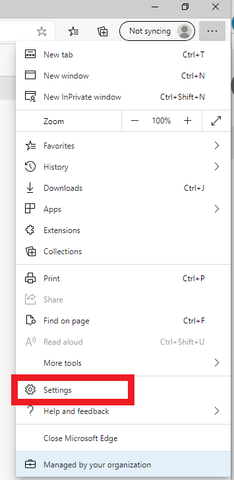
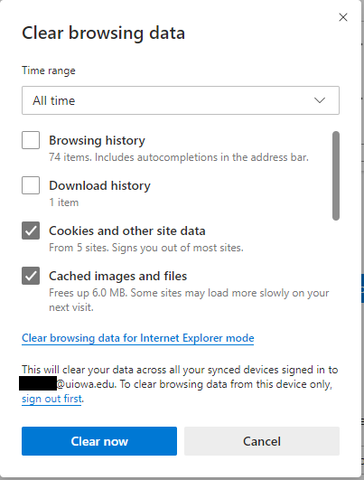
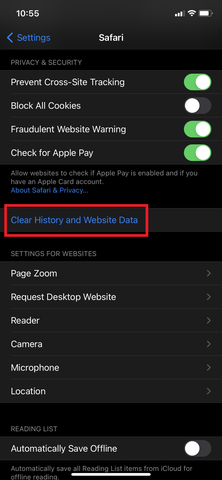
Most issues with websites (especially ones that involve pages not loading correctly/behaving in unexpected ways) can be solved by clearing out the “temporary files” that your browser holds on to from your internet travels.
The processes explained below allow you to clear these browser files out, “start fresh,” and generally resolve any issues with websites your visit that might come from those temporary files not being quite right.
Clearing your cookies may sign you out of websites you were signed into. This only requires you to sign back in, of course, but the minor inconvenience is worth thinking about before continuing.
Clearing your cache is ALWAYS SAFE! It can really only improve your situation.
Do make sure you refresh/reload any open web pages after clearing, though!
How-to Guides
On your PC
On your Phone
What are cookies?
Cookies are pieces of data from a website that are stored within the web browser, that the website can retrieve at a later time. Cookies are used to tell the server that users have returned to a particular website. When users return to a website, a cookie provides information and allows the site to display selected settings and targeted content.
Cookies also store information such as shopping cart contents, registration or login credentials, and user preferences. This is done so that when users revisit sites, any information that was provided in a previous session or any set preferences can be easily retrieved.
Advertisers use cookies to track user activity across sites so they can better target ads. While this particular practice is usually offered to provide a more personalized user experience, some people also view this as a privacy concern.
This is often how all those creepy targeted ads get data on you- One site stores a cookie saying that you looked at a product for 10 minutes and then left the site. Then Google AdSense (or another similar digital ad provider) reads the information in that cookie- and you have it recommended to you as an ad a few minutes later!
What is my ‘cache’?
You've heard the word cache before, but don't know exactly what it means in context of the Web. In common parlance, caching means placing something in storage (usually in secret) on the chance that it may come in useful later (e.g. a weapons cache). A browser or Web cache does exactly that, except with program and website assets. When you visit a website, your browser takes pieces of the page and stores them on your computer's hard drive. Some of the assets your browser will store are:
Images - logos, pictures, backgrounds, etc.
HTML
CSS
JavaScript
In short, browsers typically cache what are known as "static assets" - parts of a website that do not change from visit to visit.
What to cache and for how long is determined by the website. Some assets are removed from your machine in a few days while others may remain in your cache for up to a year.